Introduction
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s. It was discovered by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. Despite being discovered relatively recently, the ECS is deemed as one of the most crucial physiological systems involved in establishing and maintaining human health.
The Discovery:
The journey of discovering the ECS began in the mid-1960s when Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam isolated the THC molecule, leading to the elucidation of its structure and effects. However, for many years, the specifics of how THC affected the body remained a mystery.
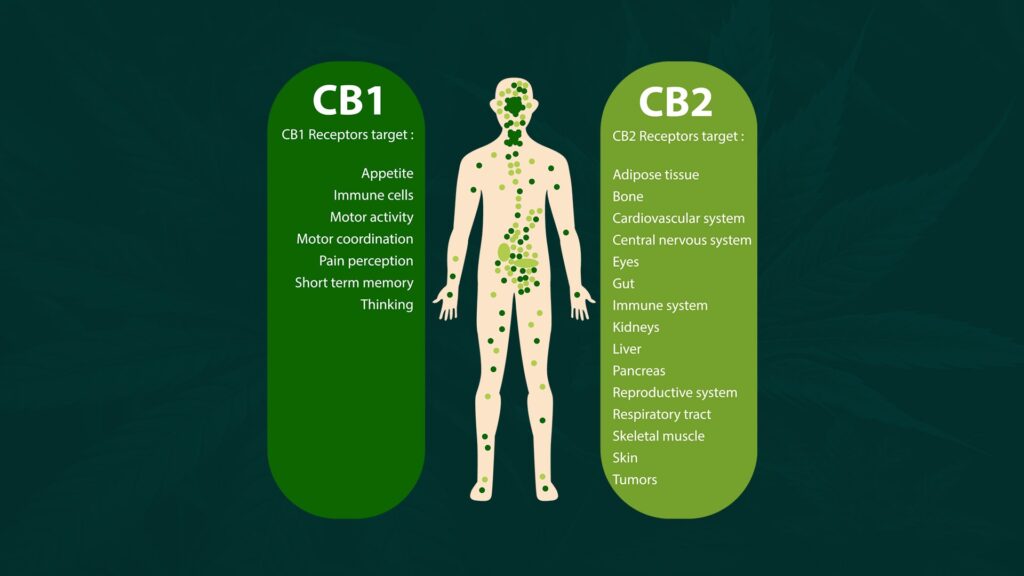
It was not until the late 1980s that Allyn Howlett and William Devane discovered the first cannabinoid receptor in a rat’s brain. These receptors proved to be more plentiful than any other neurotransmitter receptor. Soon, two cannabinoid receptors were unearthd: CB1 receptors, primarily located in the nervous system, connective tissues, gonads, glands, and organs; and CB2 receptors, primarily found in the immune system and its associated structures.
The next leap came in the 1990s, with the discovery of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), the two major endocannabinoids – cannabinoids produced naturally in the body. These endocannabinoids were revealed to engage with the CB1 and CB2 receptors similarly to cannabis-derived cannabinoids like CBD and THC.
The Research:
Research into the ECS has exploded in the last few decades, and it’s found to be flexible and adaptive. In general, the ECS can be thought of as the body’s regulatory system, maintaining homeostasis across various biological functions such as appetite, sleep, mood, pain, and much more.
Scientists believe that the overall function of the endocannabinoid system is to regulate homeostasis. Understanding ECS is becoming more critical as the medical community recognises the therapeutic benefits of cannabinoids, including THC and CBD, which interact directly or indirectly with this system.
Medical and scientific research on the ECS’s role in numerous bodily processes has advanced our understanding of its importance in disease states, including neurodegenerative disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer. It also holds the potential to provide novel treatments for conditions like chronic pain, inflammation, depression, anxiety, and addiction recovery.
Conclusion:
The discovery of the ECS has paved the way for a new understanding of the human body and its interplay with nature. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it forms a critical part of our understanding of health and disease. The ECS’s profound health implications have led to an explosion of scientific and medical research, moving beyond just understanding how THC works, to more comprehensive studies about how to harness this system’s potential for significant therapeutic advancements. As more research is conducted, we can only anticipate that our understanding of the ECS and its potential uses continues to expand.


- By Matt